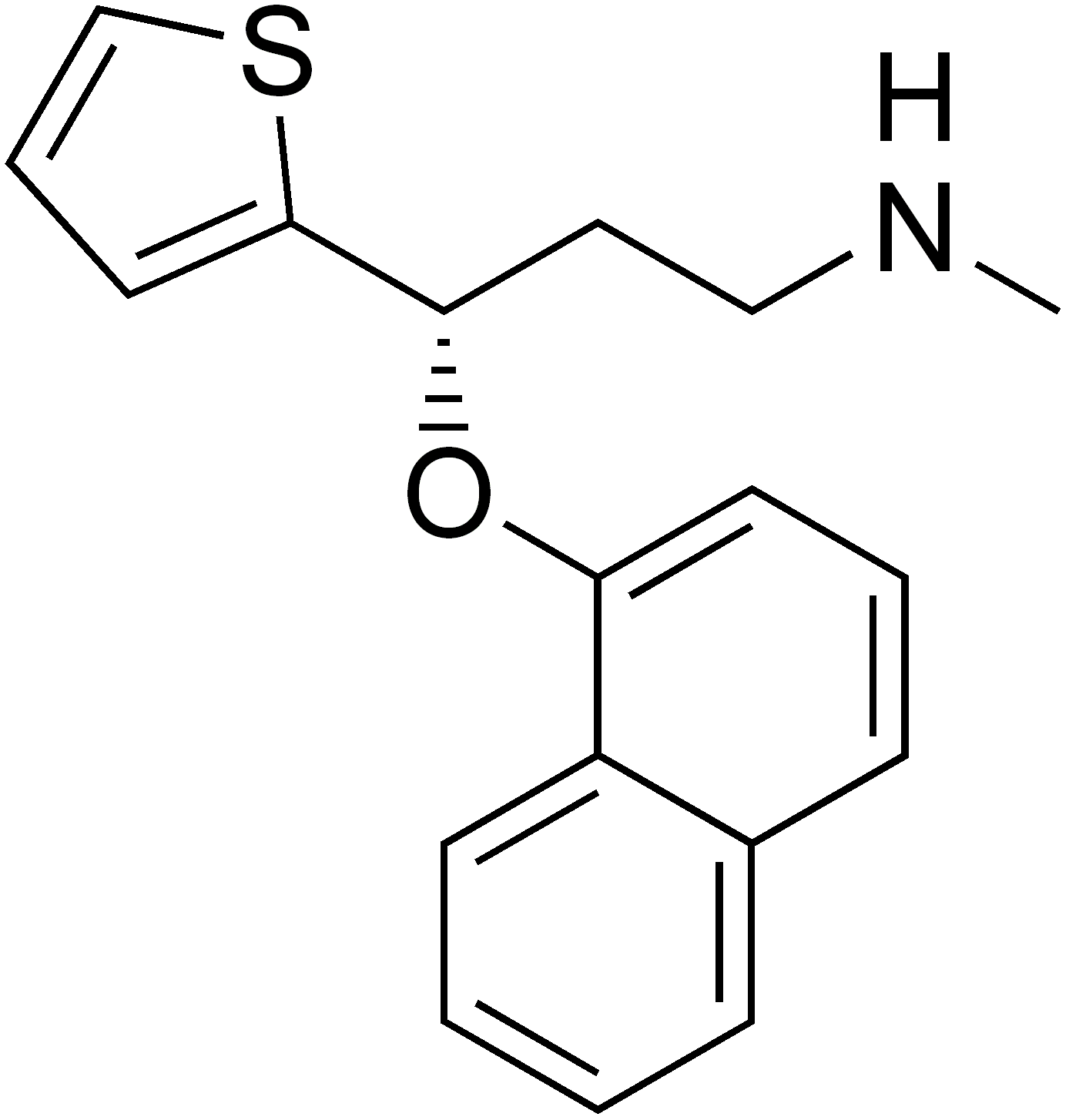
Duloxetine
| IUPAC chemical name | |
| CAS number ? |
ATC code ? |
| Chemical formula | C18H19NOS, HCl |
| Molecular weight | 333.38 |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | Hepatic Oxidation |
| Elimination half-life | 8-17 hours |
| Excretion | 70% in urine, 20% in feces |
| Pregnancy category | C (USA) |
| Legal status | Prescription only (USA) |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
Duloxetine hydrochloride (brand names: Cymbalta/Yentreve) is a medically used drug that primarily targets major depressive disorders (MDD), pain related to diabetic peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Known also as LY248686, chemically (+)-(S)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine, it is a potent dual inhibitor of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) reuptake, possessing comparable affinities in binding to NE and 5-HT transport sites. Its behavior contrasts to most other dual-reuptake inhibitors.
Furthermore, duloxentine lacks affinity for monoamine receptors within the central nervous system. While there is limited data available regarding the pharmacokinetic profile of duloxetine in humans, its half-life is reported to be 10 to 15 hours.
Duloxentine is also approved by the FDA for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy.
When used for the treatment of depression, it is commonly prescribed in doses of either 20 mg, 30 mg, or 60 mg. The long-term side-effects are unknown at this time.
External links
- Manufacturer website
- Duloxetine - medlineplus.org
- Cymbalta Mediacation Guide
- Prescribing Guide